|
|
|
| An Excellence Towards A Perfect Ness, In The Complete Denture Prosthesis - A Clinical Approach; |
Mukesh Kumar Singhal 1 , Romil Singhal 2
1 Ex Professor and Head Department of Prosthodontics - Kothiwal Dental College & Research Centre,Moradabad, UP, India
2 Student of MDS, Final Year, Department of Prosthodontics - Kothiwal Dental College & Research Centre, Moradabad, UP, India
|
| Address For Correspondence |
Mukesh Kumar Singhal,
MDS. Professor & H.O.D., Post Graduate Department of Prosthodontics,
Kothiwal Dental College & Research Centre, Moradabad, UP - 244001, India |
| Abstract |
|
|
| Keywords |
|
|
| Full Text |
Introduction
As far as, a long life of a mega structure is concerned, a well-built, solid & durable base is essential.. Our best teacher it is always our best experience likewise, Posterior palatal seal in maxilla & anterior region seal in the mandible & balanced occlusion side by side are obligatory for the success, failure & perfect ness of complete denture and underlying tissue . Present review article deals only posterior palatal seal.
Definition; it is valve seal area of soft tissue , at or along the junction of hard & soft palates on which pressure within physiological limits can be applied by denture to aid in the retention & stability of prosthesis (Fig.-1).
 | Fig 1
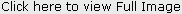 |
Aims & objectives
it is a review type article on PPS & deals to its anatomical landmarks, different types of palate & different shapes of PPS seals. Current presentation also enumerates the importance, function & process of its clinical registration.
Anatomical land marks; it extends medially from one tuberosity to another known as post dam area. It also extends laterally across the hamular notch & it travels 3 to 4 mm anteriolaterally to end in muco-gingival junction of posterior part of maxillary ridge, k/A Pterygo-maxillary seal (Fig-2). At bony level, posterior palatal seal area encompass maxillary tuberosity & hamular process of medial pterygoid plate. Land marks also contain vibrating lines.
Vibrating lines à PPS area clinically determined by an imaginary vibrating line across posterior part of palate marking division between immovable & movable tissue of the hard & soft palate.
Two types of vibrating lines exist;
• Anterior vibrating line
• Posterior vibrating line
Anterior vibrating line : it is an imaginary line, lying between immovable tissue over hard palate & movable tissue of the soft palate . It is generally cupid bow-shaped (Fig.-3).
Posterior vibrating line : it is also an imaginary line, located at junction of soft tissue that show limited movement & the soft palate that show marked movement. It is usually straight & generally having slight curvature anteriorly (Fig.-4).
Relationship of vibrating line with fovea palatine
Fovea palatine are two indentations à oval to round in shape & unique to human race located approximately1.3 mm anterior to anterior vibrating line
Importance of P.P.S;
It enhances stability & retention of prosthesis that enables the denture, to resist against, the forces of gravity, the adhesiveness of food, & the opening & closing of jaw movements. Retention is the resistance of prosthesis movement against the vertical axis. Whereas stability is the denture balance towards the horizontal axis. Retention is regulated & influenced by;
1. Peripheral border seal : It is obtained by performing border molding procedure or muscle trimming, in muco-labial and muco-buccal fold spaces so that soft tissue properly over drape to them.
2. Posterior palatal seal : Posterior border or valve seal area is completed in posterior palatal seal by border molding with the green stick compound.
Function of P.P.S; the role of PPS is related in fabrication of the special (custom) impression tray, slight displacement of palatal soft tissue, positive contact posteriorly & positioning of impression tray. The task are also enhances the quality of mastication, deglutition & phonetics. It also takes the job of food prevention under denture, eliminate gagging & sunken distal border, to counter act denture warpage & also creates a vacuum.
 | Fig 2
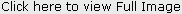 |
TYPES OF PALATES ; two type -
· Hard palate – Anterior part
· Soft palate - Posterior part
Classification of Hard Palates;
l Class A - broad, shallow, and flat palate, & least beneficial.
l Class B - v-shaped, medium vaulted palate. It gives intermediate quality of P.P.S.
Class C- high vaulted & U-shape, it gives best retention and stability so most helpful P.P.S (Fig.-5).
Classification of Soft Palates;
l Class I - it is horizontal & makes 10° angle to the hard palate & most advantageous (Fig.-6).
l Class II - soft palate makes a 45° angle to the hard palate.
l Class III -soft palate makes a 70° angle to the hard palate.
 | Fig 3
 |
Categorization Of Palatal Seal ;
· According to shape - generally five shape recommended.
1. Single bead shape of posterior palatal seal
2. Double bead shape of P.P.S.
3. Butter-fly shaped of P.P.S.à best retentive effect (Fig. -7).
4. Butter-fly shaped P.P.S, with bead on distal angle of dentures.
5. Butter- fly shaped of P.P.S, with widened on distal angle of dentures.
· ACCORDING TO AREA COVERED; It is according to palatal throat form between the hard and soft palatal area as follows,
Class Ι à large and normal in form, an immovable band of tissue 5 to 12 mm distal to across the line of maxillary tuberosity.
Class ΙΙà immovable band of resilient tissue - 3 to 5 mm.
Class ΙΙΙ à with small maxilla, curtain of soft tissue abruptly down 3 to 5 mm.
Choice Of P.P.S. Width; anterio-posteriorly - Enough wide à3 to 4 mm wide & while at Hamular notch à2 to 4 mm wide. The dept of P.P.S. is 1 to 1.5 mm in height and 1.5 mm at its base in case of a bead type.
Recording of P.P.S. clinically; it is performed by conventional method, fluid wax method & arbitrary scribing of master cast.
Conventional method; it is accomplished by marking with the indelible pencil, at pterygo-maxillry seal by using “tZ0;burnisher. Recording of anterior vibrating line is performed by valsava manner & whereas posterior vibrating line by asking “ah’ in vigorous manner. This is technique-sensitive method.
FLUID WAX METHOD; It is done by using Correcta wax no: 4, or adaptor wax and physiologic paste. It is physiologic & chair time consuming technique.
ARBITRARY SCRIBING OF MASTER CAST; this technique is inaccurate & non physiological.
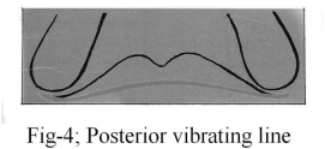 | Fig 4
 |
Summary & Conclusion;
Perfection is achieved, not when there is nothing more to add but when there is nothing left to take away. Incorporation of posterior palatal seal is a paramount & extremely important. It provides state of art technology & enhances stability & retention of a maxillary RDP. A butter-fly shaped P.P.S. posses maximum retentive effect; moreover its width varies from 2 to 5 m.m.
References;
1. Hardy IR & Kapur kk: “posterior border seal & its rationale & importance”. JPD 8; 386 – 7, 1958.
2. Hold HR: “variable denture limiting structure of the edentulous mouth”. JPD 9:978, 1959.
3. Landa JS: “Trouble shooting in complete denture prosthesis.” JPD 9:978, 987, 1964.
4. Milsap CH: “Posterior palatal seal area for complete denture. Den. Clin. N.AM 8:663, 673, 1964.
5. Kabcenell JI: “more retention of complete denture.” JADA 80: 116 1970.
6. Silverman SJ: “Dimension & displacement patterns of PPS” JPD. 25:470, 488 1971.
7. Winland RD & Young JM: “Maxillary complete denture, Posterior palatal seal variations’’. JPD 29:256, 261, 1973.
8. Avant WE: “A comparison of retention of complete denture bases having different type of posterior palatal seal.” JPD 29: 484, 493 1973.
9. Lye TL.“ significance of fovea palitini in complete denture. JPD 33: 504 May 1975.
10. Ames WVB. Atmospheric pressure in retention of entire denture.” BDJ 6: 601-604, 1985.
11. Glossary of prosthodontics terms(GPT) JPD 1977, May 2005 and article publication guide line - 2008. |
|
|
|
|
|
|