Introduction
Flexible denture can be used for the patient having few teeth or at-least two teeth in both side of arch .It can be used even in case with teeth present unilaterally in arch using extended clasp. The application of nylon like material for the fabrication of dental appliances replaces the acrylic and metal to build the framework of removable partial denture.
Thermoplastic materials for dental prosthesis , Valplast (Valpalst int. Corp USA) and Flexiplast (Bredent) were first introduced to dentistry in 1950. Both materials were similar grade of polyamides (nylon plastic) rapid injection systems ( Flexible company USA) originated in 1962. Valplast introduced a flexible same translucent thermoplastic resin to create flexible tissue born partial denture. Acetal was first proposed as an unbreakable thermoplastic resin for removable partial denture in 1971. In 1986 tooth coloured clasp was introduced. The clasp was flexible. In 1992 Flexite company developed the first preformed tooth coloured clasp.
Applications of thermoplastic resin are 1) Removable partial denture 2) Provisional crown and bridge 3) Obturator and speech therapy appliance 4) Orthodontic retainer and bracket 5) Impression trays 5) Border moulding material 6) occlusal splint 7) Implant abutments
Case
Patient with age 65 years old came to Panineeya dental collage with the teeth present unilaterally 13,14,15 and 34,35,36,37 Kennedy's class I and class II. Patient wanted a replacement of teeth by removable partial denture. As the patient was very old and medically compromised implant supported denture were not considered. As the teeth are very less in number and present unilaterally, the flexible denture with wrap around distal clasp was fabricated for the patient by engaging the undercut
Method
1. Primary impression was made with irreversible hydrocolloid impression material.
2. Custom tray was made with 2mm wax spacer.
3. Elastomeric impression material with light body and putty was made
4. Duplication of master cast was done with the die stone
5. Jaw relation was made
6. Teeth set-up :- no less than 1\3 of the teeth neck be inserted into modelling wax. V-shaped channels were created on the tissue side of the tooth
7. The duplicated model was waxed up and cut with the special saw or disk as close to the wax as possible
8. Special flask with bolts was used .The lower half of the flask was filled with stone and covered the model
9. Sprues were connected to the wax pattern a) Sprues should be straight .b) A sprue should be thinner at the connector. c) Minimum 3 sprue should be present one on each distal side and one in the middle of the connector
10. Flask was closed using bolts to allow opening it easily after dewaxing
11. Upper half of the flask was filled with stone through opening
12. Dewaxing was performed for 15 min in boiling water
13. The cartridge was heated at 285 degree Celsius and injected in to the flask with Valplast machine
14. Flask was Bench cooled, the denture was taken out, trim and polish it with polishing bur
Disscussion:
Flexible dentures exhibit high creep resistance, fatigue resistance as well as excellent wear characteristic and solvent resist ance .There is no free monomer and porosity with less odour and stain. It has got higher dimensional and colour stability. Thermoplastic nylon is a resin derived from diamine and dibasic acid monomer . Nylon exhibits high physical strength, heat resistance and chemical resistance .Because of its inherent
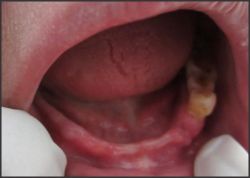 | Fig.1 Shows Kennedy's class II
 |
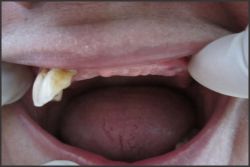 | Fig.2 Shows Kennedy's class I
 |
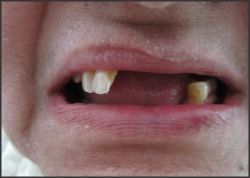 | Fig.3 Shows maxillary and mandibular edentulous arches
 |
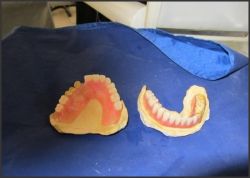 | Fig.4 Shows flexible dentures on casts
 |
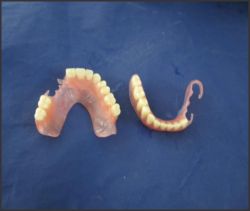 | Fig.5 Shows maxillary and mandibular flexible dentures
 |
flexibility, it is used primarily for flexible tissue born partial denture .It does not have enough strength to use for occlusal rest seat ,and won't maintain vertical dimension when used in direct occlusal forces .Thermoplastic nylon is injected at temperature from 274 to 293 degree Celsius and has a specific gravity of 1.14 ,mould shrinkage amount to 0.014 inch\inch ,tensile strength is 11000 psi and flexural strength is 16000psi. Nylon is little more difficult to trim and polish. The resin is semi translucent and provide excellent aesthetic for flexible tissue borne partial denture
Valplast is nearly unbreakable, is coloured pink like a gum, can be built quite thin, and can form not only the denture base, but the clasp as well. Since clasp are built to curl around the neck of the tooth, they are practically indistinguishable from gums that surrounds the teeth. Even though this denture dose not rest on the natural teeth like cast partial denture , the clasp rest on gum surrounding the natural teeth. This type of partial denture is extremely stable, retentive and elasticity of the clasp keeps them that way indefinitely. Flexite supreme's base component is co-polyamide. It is easy to adjust and polish. Flexite is used to fabricate removable partial denture, TMJ disfunction, bruxism, anti- snoring device, sport mouth guards, tooth coloured clasp. Flexible thermoplastic materials is available in three tissue shades. The material is monomer free, unbreakable, light weight and impervious to oral fluids. Flexite plus may also combine with a metal frame work to eliminate the display of metal labially
Summary
Flexible dentures fabricated by using Valplast nylon resin are derived from diamine and dibasic acid monomer. Valplast exhibits high physical strength, heat resistance and chemical resistance. It has got good stiffness and wear resistance but it cannot be used as an occlusal rest as in cast partial denture. It is used primarily as a tissue borne flexible partial denture. Valplast is slightly difficult to adjust and polish. In this case teeth are present unilaterally, so better option was flexible partial denture by using wrap around distal clasp . The denture had a better retention and stability.
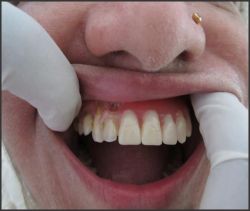 | Fig.6 Shows maxillary denture in patient's mouth
 |
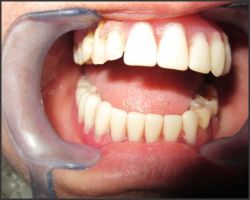 | Fig.7 Shows maxillary and mandibular dentures in patient's mouth
 |
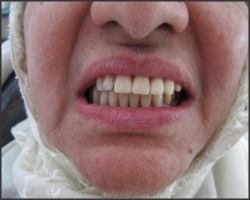 | Fig.8 Shows maxillary and mandibular dentures in occlusion
 |
Conclusion
Whenever there are unilateral teeth remaining with minimal undercuts, by using wrap around clasp we can fabricate a good flexible partial denture. As the patient was very old and medically compromised implant was not considered. In this case there was a good retention, light weight, better esthetics and comfortable to the patient comparable to cast partial denture.
Reference
1. Lowe LG: Flexible denture flanges for patients exhibiting undercuts, tuberosities and reduced width of buccal vestibule: a clinical report: J Prosthet Dent 2004;13(1);17-27
2. Keenan PL, Radford DR, Clark KF: Dimensional change in complete denture fabricated by injection moulding and microwave processing : J Prosthet Dent 2003; 89(1);37-44
3. John J, Gangadhar SA, Shah I: Flexural strength of heat-polmerized polymethyl methacrelate denture, resin reinforced with glass, aramid or nylon fibres : J Prosthetic Dent 2001;86(4) 424-7
4. Anderson GC, Schulte JK, Arnold TG,: Dimensional stability of injection and conventional processing of denture base acrylic resin : J Prosthet Dent 1988;60:394-8
5. Beaumont AJ Jr.: An overview of esthetics with removable partial denture Quintessence Int. 2002;33(10):747-55
6. Nogueria SS, Ogle RE, Davis EL: Comparision of accuracy between compression and injection moulded complete dentures.J Prosthet Dent 1999;82:291-300
7. Parvizi A,Lindquist T, Schneider R et al: Comparison of dimensional accuracy of injection moulded denture base material to that of conventional pressure pack acrylic resin J Prosthodont 2004;13(2);83-9
8. Pardo-Mindan S, Ruiz-Villan Diego JC: A flexible lingual clasp as an esthetic alternative: a clinical report: J Prosthet Dent 1993;69:245-46
9. Salim S, Sadamori S, Hamanda T: The dimentional accuracy of rectangular acrylic resin specimens cured by three denture base processing methods;J Prosthet Dent 1992;67;879-81
10. Wong DM, Cheng LY, Chow TW: Effect of processing method on dimentional accuracy and water sorption of acrylic resin denture : J Prosthet Dent 1999;81:300-4
11. Wostmann B, Butz-Jorgensen E, Jepson N, et al: Indication for removable partial denture: a literature review: Int.J Prosthodont 2005;18(2):139-45 |